Which Job Can a Capacitor Perform in Electrical Work?
What is the role of a Capacitor in Electronic Components? Focusing on the mechanism
Perfect partner for electronics
Nearly electronic devices employ capacitors that are an invaluable part of electronic products. Capacitors are very pop among many applications like electronic circuits, power circuits, and power supply units.
The capacitor is referred to as Big Three Passive Components together with resistance and coil, which are the basics of electronic circuits. Passive components are the electronic part that receives the power to consume, store, and supply.
Unlike integrated circuits (IC), it has no active functioning where low power is amplified to output the power constantly. You might as well regard a capacitor as a simple part to receive and supply the electricity. Yet, more importantly, such passive components are indispensable parts to perform agile components accurately.
The Three Passive Components are also called LCR, which stands for Whorl, Capacitor, and Resistance.
Consisting of two metal plates and insulator, Basic model of capacitor
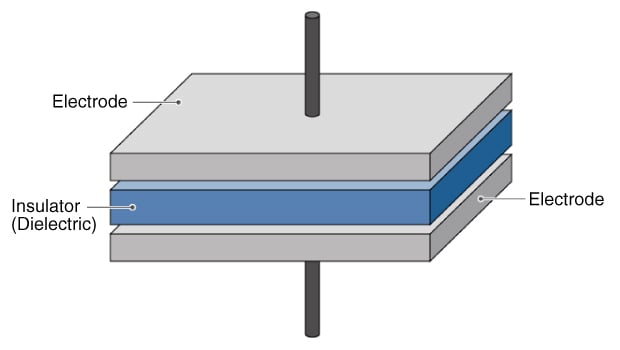
Capacitor is basically formed from an insulator and two metallic plates that are attached on both sides of the insulator. Insulators do not comport current. The insulator used for capacitors is specifically called dielectrics. While the electricity is flowing, the positive and negative charges are transferred within the usher.
Charged with the electricity, the menstruation of the charge is started, but it is blocked since there is an insulator between metal plates. Then, the charges are built upon only one of the 2 metal plates. Meanwhile, some other metal plate attached to the insulator has an opposing charge.
Thus, capacitors have a structure to store the electricity between the 2 metal plates. For materials of insulator, gases, oils, ceramics, and resin are used. As for the shapes of the metal plates, there are a wide diverseness of types with parallel plates, foil wrapping, multi-layers, and so on. The amounts of stored charges, as well as the supported frequencies, are different depending on the types of insulators or the construction of capacitors. So, it is necessary to select a suitable capacitor to meet your requirements.
Importance of Capacitors
In the principle of capacitors, there are two important parts.
- Storing the electric accuse (electricity)
- Air conditioning flowing simply not DC
For details regarding storing electricity, please refer to the above-mentioned Basic construction of a capacitor.
Equally the electric accuse is stored between the metallic plates, the electric charge transfer is stopped, making DC stop flowing. Yet, in other words, until capacitors are fully charged, even DC tin flow for a short period of fourth dimension. In the case of AC, the current direction is switched with a sure interval, and so a capacitor is charged and discharged. Therefore, the electricity looks like passing through the capacitor.
Appropriately, the college the AC frequency is, the easier the passing is through capacitors. Thus, capacitors play the three post-obit important roles in the electronic circuit.
1) Charging and discharging electric charges
Capacitors tin can charge and discharge considering of the structure. Featured past the electric charge and discharge, capacitors too can exist used every bit a ability supply. Camera flashes utilize this characteristic of capacitors.
In order to have strong low-cal-emitting, a high voltage must be instantly applied to it. Meanwhile, such a high voltage is not required in the excursion to operate the camera. Then, there is a suitable structure of a capacitor where such high calorie-free emission is provided by instantly discharging the electrical charge stored in the capacitor.
ii) Keeping the voltage at the same level
Apart from the above feature, capacitors likewise take functions to keep the voltage at a certain level. Capacitors are useful to reduce voltage pulsation. When the loftier voltage is applied to the parallel excursion, the capacitor is charged, and on the other hand, it is discharged with the depression voltage.
While electricity flowing out is alternating current, about electronic circuits piece of work with direct current. Therefore, Ac is converted to DC via a rectifier circuit which changes AC to DC, but the converted DC is an unstable current with ripples at this stage. To deal with this, a capacitor is used to correct the ripples and keep the voltage constantly.
iii) Removing noise
In terms of noise reduction, the feature in a capacitor of flowing AC but DC is useful for removing noise. In general, as the noise in DC is an AC component with high frequency, information technology has a tendency to get through the capacitor hands.
By inserting a branch excursion betwixt the input and output, the ground is formed to connect to the capacitor. Post-obit this, the AC component only goes through the capacitor, and and so DC flows in the output circuit.
Types of Capacitors
- Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor
- The capacitor is fabricated from aluminum and another metallic. Every bit oxide moving picture blocks the electricity, it is used as a dielectric fabric by forming on the surface of the aluminum. This type of capacitor offers large capacitance at an affordable price. Therefore, it has widely been used as a large-capacity capacitor. Nonetheless, it has some weak points like bad frequency characteristics, larger size, the loss of dielectric due to liquid leakage.
- Tantalum Capacitor
- The capacitor uses tantalum for the anode and tantalum pentoxide for the dielectric material. It has a relatively large capacitance while information technology is smaller in size than an aluminum electrolytic capacitor. Furthermore, the capacitor is superior to the aluminum capacitor in terms of leakage current characteristics, frequency property, capacitors, and temperature characteristics.
- Electrical Double Layer Capacitor
- Electrical double-layer capacitors characteristic an extremely large capacitance. It is more than 1,000 times to ten,000 times greater than aluminum electrolytic capacitors, and it can exist used repeatedly for a long menses without limitations such as the number of charge/discharge cycles. Taking advantage of the unique characteristic, the capacitor tin can exist used repeatedly. Electric double-layer capacitors have electric charges oriented at the boundary of electrolyte and electrode, which is called "electric double-layer" with the size of a single molecule. The layer is used equally the dielectric material of double-layer capacitors. The toll of electric double-layer capacitors is relatively high compared to the other ones.
- Ceramic Capacitor
- The capacitor is largely divided into 3 types based on the types of ceramics used equally dielectric materials: low dielectric blazon, high dielectric blazon, and semiconductor blazon. Equally a main feature of the capacitor, the increasing voltage changes its capacitance. The small capacitor is heat-resistant, although it is frail and could be chipped or broken.
- Film Capacitor
- In this blazon, films such as polyester and polyethylene are used equally the dielectric fabric. Polyester, polypropylene, and other films are sandwiched between the electrode foils on both sides, and they are wound into a cylindrical shape. The not-polar capacitor that is larger than the ceramic capacitor has loftier insulation resistance and no electric loss. It also provides loftier reliability with first-class properties in frequency and temperature.
- Mica Capacitor
- The capacitor uses mica, which is a natural mineral, as the dielectric material. Mica is ideal for the capacitor as it has a high dielectric property and can be peeled off. Mica capacitors have excellent characteristics such as insulation resistance, dielectric loss tangent, frequency, and temperature characteristics, although in that location are some disadvantages in that they are expensive and big-sized units.
For more than information about types of capacitors, delight refer to the link below.
Types of capacitors. Bones component knowledge
Recommended products
Source: https://www.matsusada.com/column/capacitor.html
0 Response to "Which Job Can a Capacitor Perform in Electrical Work?"
Post a Comment